Problem Tree
Problem Tree Analysis: A Complete Guide to Root Cause Problem Solving
Problem Tree Analysis gives you a framework to map out the causes and effects of a problem, helping you visualize how various issues are connected that led to your current situation.
Before we discuss the problem tree in detail, let’s talk about a few problems.
- Which of these complex challenges are you facing in your business?
- Target revenues falling short despite increased market spend
- Employee productivity is dropping even with new systems in place
- Rising customer complaints despite quality improvements
All these problems share a common thread: treating symptoms instead of identifying root causes.
When such challenges occur, teams opt for quick fixes with traditional problem-solving approaches. During all this, the underlying issues, the real culprits, are left unaddressed.
To counteract, we have problem tree analysis, a solution that offers a structured analysis. Organizations can move beyond surface-level symptoms to tackle fundamental issues.
How?
By mapping problems visually and systematically identifying cause-and-effect relationships.
This guide helps you find out how this method transforms overwhelming challenges into manageable components by enabling your teams to focus their efforts where they’ll have the greatest impact.
This guide helps you find out how this method transforms overwhelming challenges into manageable components by enabling your teams to focus their efforts where they’ll have the greatest impact.
What is Problem Tree Analysis?
This structured problem-solving method visualizes problems as a tree diagram. The core issue lies at the center and its causes, like a tree’s branches spread across. It’s creating a visual map of how different factors contribute to the central problem, making complex issues easier to understand and solve.
So, what is the benefit, you might wonder? This analytical approach transforms abstract problems into concrete and actionable insights by breaking down big issues into manageable concepts.
Usually, teams are overwhelmed by seeing a massive problem. With a problem tree, teams can systematically identify what’s actually causing it.
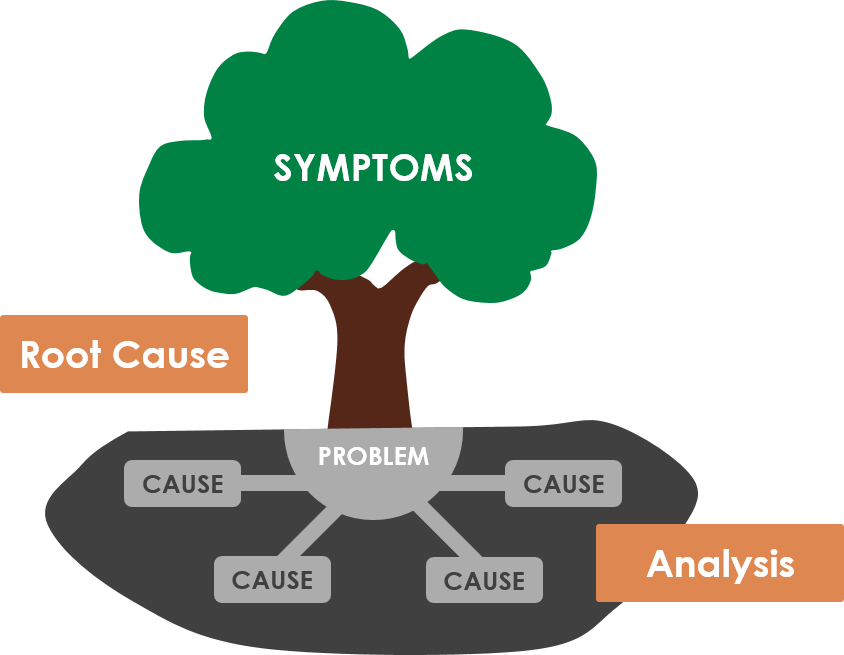
Below is a typical example of a problem tree diagram.

Understanding the Problem Tree Structure
A problem tree diagram follows a logical hierarchy, forming a visual structure. It immediately clarifies how different elements relate to each other and where to focus your problem-solving efforts.
The Trunk (Core Problem) | The main issue sits in the center. This is what you’re trying to solve. |
The Roots (Causes) | Causes branch out at different levels below the trunk. Direct causes connect immediately to the problem. Underlying causes feed into these direct causes. |
The Branches (Effects) | Above the trunk, you’ll find the consequences and impacts of the problem. |
When to Use Problem Tree Analysis
This is the best tool if you have been facing:
- Multi-faceted problems with unclear causes
- Team-based problem solving where different perspectives collide and need integration
- Recurring issues that keep coming back, no matter what immediate fixes you have been attempting
- Strategic planning requires a proper understanding of barriers to success
- Process improvement initiatives in the operational environment
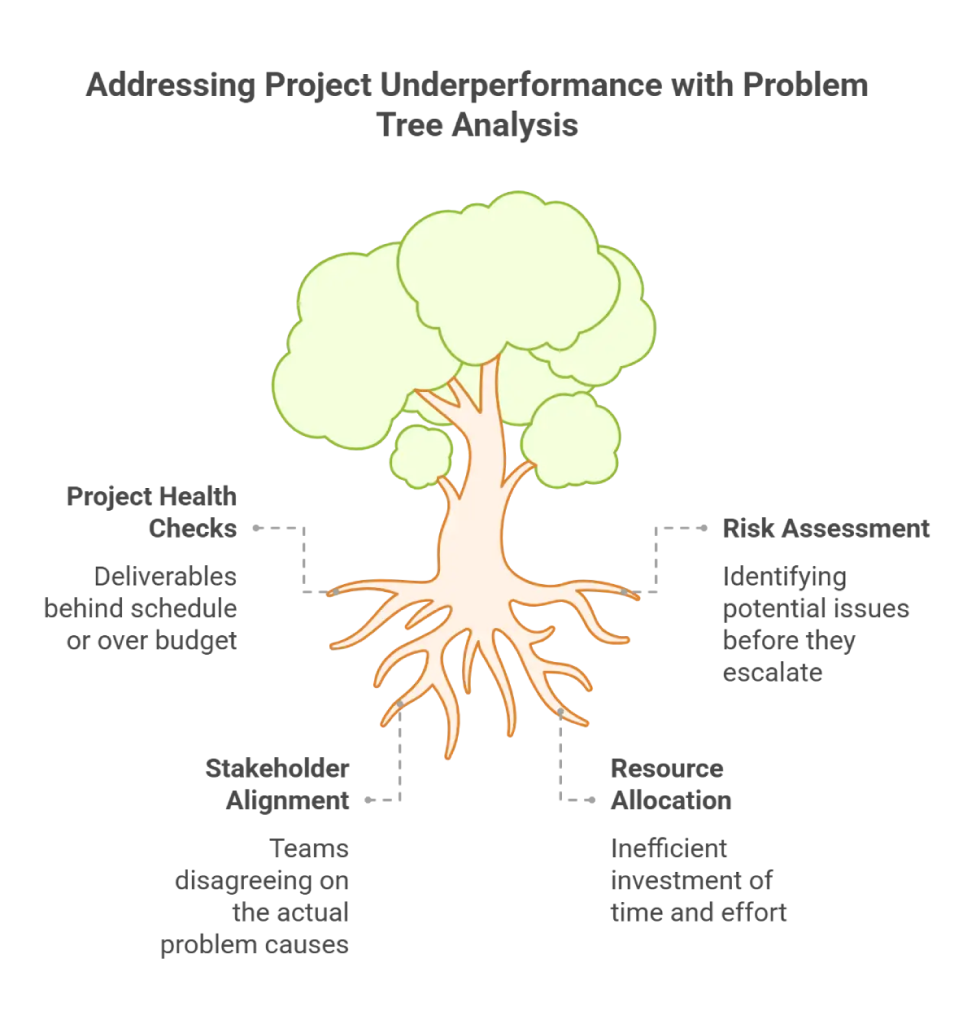
Problem Tree Analysis in Project Management
The scope of problem tree analysis in project management can’t be neglected. Project managers use it as a diagnostic tool when projects face challenges such as underperformance.
Here’s how this diagnostic tool can be used in organizations to move beyond surface-level symptoms and address fundamental issues.
How Management Consulting Uses the Issues Tree Method
Management consulting firms significantly rely on issue tree problem-solving since it brings structure to an ambiguous business challenge. They believe this approach transforms vague concerns into clear, actionable plans.
Let’s see how they use this to identify problems:
- Break down complex business problems into specific, measurable components
- Identify root causes rather than just treating symptoms
- Create a focused recommendation based on actual problem drivers
- Facilitate productive discussions with client teams about priorities
The Problem-Solving Tree Method: Step-by-Step Process
Step 1: Define Your Core Problem
- Start with a clear and specific problem statement.
- Avoid vague descriptions like “things aren’t working well.”
- Use concrete statements like “customer satisfaction scores dropped 15% in the last quarter.”
Step 2: Identify Direct Causes
- Ask “What directly causes this problem?”
- These first-level causes should have an immediate, obvious connection to your core issue.
Step 3: Dig Deeper Into Root Causes
- Ask “What causes this?” for each direct cause.
- Continue with this process until you reach fundamental root causes that can’t be broken down further.
Step 4: Map the Relationships
- Draw connections between causes to show how they interact and reinforce each other,
- Some causes might contribute to multiple problems
Step 5: Prioritize and Validate
- Note that not all causes are equally important.
- Focus on the causes that have the biggest impact and are most feasible to address.
Problem Tree vs. Other Analysis Methods
- Problem Tree vs. Fishbone Diagram
Fishbone diagrams categorize causes by type, for example, process, people, and environment. Whereas problem trees show hierarchical relationships between causes.
- Problem Tree vs. 5 Whys
The 5 Whys technique follows a single chain of causation. A problem tree, on the other hand, maps multiple interconnected causes simultaneously.
- Problem Tree vs SWOT Analysis
SOWT focuses on strategic positioning, while problem trees are all about specific operational issues.

Common Mistakes to Avoid With Problem Tree Analysis
- Going Too Broad: You might lose track of doing so. It’s suggested to keep your core problem statement focused and specific.
- Confusing Causes With Effects: Don’t stop at the first layer of causes. Keep investigating until you reach the issues at the root.
- Ignoring Interconnections: Remember, problems rarely have single causes. Look for how different factors reinforce each other.
Making Problem Tree Analysis Work for Your Organization
So, now that you have got your hands on a practical, analytical tool, here’s the final takeaway for you:
- Start with smaller and well-defined problems to build confidence with the method.
- Involve stakeholders with a better understanding of different aspects of the issue.
- Use the analysis as a foundation for developing targeted action plans
Following the plan can help you experience the most successful problem tree analysis that leads directly to specific and actionable solutions, addressing the root causes.
Got Something to Share About Problem Tree Analysis?
We’d love to hear from you. Experiences, insights, and latest info on different topics are all welcome in our dedicated space for experts.
Let’s get in touch to spread awareness about Problem Tree Analysis.
FAQs
- What is the tree method of problem-solving?
It’s a visual technique that breaks down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts by drawing them like a tree structure. The main problem sits at the trunk, the root causes spread out below like roots, and the effects branch out above, just like branches.
- How do you create a problem tree analysis?
Here’s what you should do:
- Start writing your main problem in the center
- Brainstorm and write all causes below it, like the roots of a tree
- Write all the effects or consequences above, like branches
- Connect related causes and effects with lines to show how they link together
This will help you visualize the problem with clarity.
Latest Article & Content
- Plant Inspections and lubrication schedule
- Breakdown maintenance
- Cost reduction programs
- Improving Oee in Business Operations
- Toll Production and Production Outsourcing
- Country and Work Culture in South east Asia
- Discounted Payback period
- Payback Period
- Cycle Time Optimization: How to Boost Production Flow and Output
- Cycle Time vs Takt Time
- The Complete Guide to Lead Time Calculation
- What Are Two Characteristics of Lean Manufacturing?
- Benefits of Lean Manufacturing
- 10 Proven Ways to Reduce Lead Time in Manufacturing
- 7 Real-World Examples of Lean Manufacturing
- How Do You Get Certified In Lean?
- How to Choose Flowchart Symbols: A Complete Guide for Lean Manufacturing Professionals
- What are The 4 Pillars of Lean?

