Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
All too often, businesses face a feared situation. What seems like a perfectly running manufacturing facility witnesses the breakdown of the most critical production line or machine. The repair takes hours, the delivery schedule is shot, and the costs start to spiral higher and higher to get orders to customers.

Have you been in such a situation? If yes, we’ve got a proven framework that can become a solution to this situation. This is where Total Productive Maintenance or TPM becomes a game-changer for manufacturers worldwide.
What Do We Define as TPM or Total Productive Maintenance?
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a comprehensive approach to equipment maintenance that aims to achieve:
Zero defects | Zero equipment failures |
Zero accidents in manufacturing operations | |
Unlike traditional maintenance strategies that focus on fixing problems after they occur, Total Production Maintenance in manufacturing empowers every employee to take ownership of equipment health and performance.
When everyone prioritizes machine health and condition, that’s when real transformation truly begins.
TPM: The Evolution from Reactive to Productive Maintenance
Traditional maintenance followed a simple rule: run equipment until it breaks, then fix it. This is usually called breakdown maintenance. Modern manufacturing, on the other hand, demands much more than this approach.
Total maintenance productive strategies recognize that in today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape, unplanned downtime isn’t just inconvenient but potentially catastrophic.
TPM in industry emerged from this need for a more proactive and holistic approach. It transforms maintenance from an overwhelming and necessary to-do into a competitive advantage.
Core Principles of TPM Manufacturing Excellence
1. Equipment Effectiveness Maximization
The core of any TPM manufacturing program involves maximizing Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). In simpler words, this means focusing on three critical areas:
Availability: Minimizing downtime and stoppages
Performance: Maintaining optimal production output speed and efficiency
Quality: Reducing defects and rework
2. Autonomous Maintenance
Here’s where TPM gets transformative. Operators become the first line of defense, rather than waiting for the maintenance technicians to address the problem. They perform routine inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and minor adjustments.
You shouldn’t confuse it with replacing skilled technicians. It focuses more on creating a more responsive maintenance ecosystem.
3. Planned Maintenance Excellence
While operators handle everyday care, skilled maintenance professionals focus on complex planned maintenance activities.
This includes predictive maintenance using advanced technologies, major overhauls, and continuous improvement initiatives.
The Eight Pillars of TPM Success
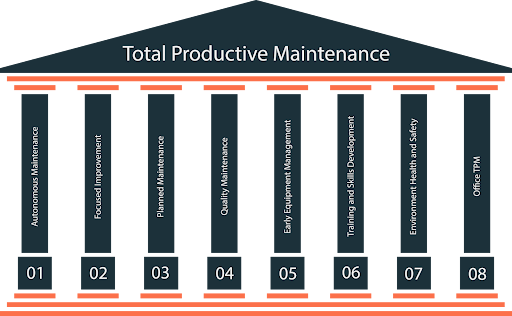
Total Productive Maintenance stands on eight foundational pillars. Each pillar addresses different aspects of manufacturing excellence:
Pillar 1: Autonomous Maintenance | Operators take ownership of basic maintenance tasks. They develop deep equipment knowledge and take pride in their machines. |
Pillar 2: Planned Maintenance | Systematic approach to maintenance scheduling, spare parts management, and well-planned major maintenance activities. |
Pillar 3: Quality Maintenance | Eliminating quality defects at their source by maintaining equipment in optimal condition. |
Pillar 4: Focused Improvement | Continuous improvement activities targeting specific losses and inefficiencies. |
Pillar 5: Early Equipment Management | Incorporating maintainability and reliability into new equipment design and installation. |
Pillar 6: Training and Education | Building maintenance competencies across all organizational levels. |
Pillar 7: Safety, Health, and Environment | Creating safer, cleaner, and more environmentally responsible operations. |
Pillar 8: Administrative and Office TPM | Extending concepts to support functions and administrative processes. |
TPM and Lean Manufacturing: Perfect Partners
Lean TPM represents the powerful combination of Total Productive Maintenance with lean manufacturing principles. This integration creates synergies that neither of these approaches can manage to achieve alone.
In Lean TPM implementations, maintenance activities are optimized for:
Waste Elimination: Removing non-value-added maintenance activities
Flow Optimization: Ensuring maintenance doesn’t disrupt production flow
Pull-Based Systems: Performing maintenance based on actual need rather than imaginary schedules
Continuous Improvement: Using Kaizen events to refine maintenance processes constantly
Practical Benefits of TPM Implementation
We have brought you real-world stats and figures related to TPM implementation. Companies with TPM in industry have documented significant improvement through various case studies and research:
Equipment Performance:
Most companies realize a 15-25% increase in equipment efficiency rates within three years of adopting TPM (US EPA)
Case studies show breakdown reductions of 23% for CNC lathes and 38% for CNC machining centers
OEE improvements from 81.65% to 85.75% in nail production lines
OEE improvements from 75% to 85% in polymer manufacturing
Cost Impact:
Maintenance activities typically account for 15% to 40% (average 28%) of total production costs, providing substantial savings potential
Reduced emergency repair expenses through preventive maintenance
Optimized spare parts inventory and maintenance schedule
Cultural Transformation:
Enhanced employee engagement and equipment ownership
Improved communication between operations and maintenance teams
Stronger safety culture and environmental consciousness
Getting Started: Your TPM Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-6)➡️Secure leadership commitment and establish the TPM steering committee ➡️ Conduct baseline assessments of current maintenance practices ➡️ Select pilot areas for initial implementation ➡️ Begin basic TPM training for all personnel, including its benefits | Phase 2: Autonomous Maintenance Launch (Months 4-12)➡️ Implement the seven steps of autonomous maintenance ➡️ Develop standard operating procedures for routine maintenance tasks ➡️Create visual management systems and equipment checksheets ➡️ Establish small group improvement activities |
Phase 3: Planned Maintenance Optimization (Months 8-18)➡️ Implement preventive and predictive maintenance programs ➡️ Optimize maintenance schedules and work order systems ➡️ Develop maintenance skills and competencies ➡️ Focus on equipment reliability improvements | Phase 4: Advanced TPM (Months 12-24)➡️Expand TPM to all remaining equipment and areas ➡️ Implement quality maintenance and early equipment management ➡️ Develop internal TPM expertise and sustainability mechanisms ➡️ Measure and celebrate continuous improvement achievements |
TPM Challenges and Overcoming Them
Resistance to Change:
This is one of the most significant of TPM challenges. Workers are usually reluctant to embrace the new change.
Solution:
Start with willing participants and demonstrate early wins. Success stories are your best change agents.
2: Lack of Time for Training
Since the operations are already running, often manufacturers find it difficult to spare time for training.
Solution:
Integrate TPM training into daily work activities. Make learning a part of the job without separating it from daily activities.
3: Sustaining Momentum
Often, businesses too enthusiastic about TPM slow down and find it hard to sustain the momentum.
Solution:
Establish clear metrics, regular reviews, and recognition systems.
Technology’s Role in Modern TPM
TPM Manufacturing is incomplete without leveraging the following advanced technologies:
IoT Sensors ensure real-time equipment monitoring and predictive analytics
Mobile Applications handle digital work orders and maintenance tracking
Augmented Reality focuses on enhanced training and troubleshooting capabilities
Artificial Intelligence is all about predictive maintenance, optimization, and failure pattern recognition
Measuring TPM Success
Effective TPM in manufacturing requires robust measurement systems. Manufacturers can employ the following to measure their TPM success.
Leading Indicators:
Training completion rates and skills matrixes
Autonomous maintenance compliance
Number of improvement suggestions implemented
Lagging Indicators:
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
Maintenance cost per unit produced
Safety incident rates
The Future of TPM in Industry
With increasing digitalization, manufacturing also becomes more digital and connected. TPM in industry evolves likewise.
Further developments in TPM include:
Integration with Industry 4.0 technologies
Advanced predictive analytics and machine learning
Remote monitoring and maintenance capabilities
Sustainability-focused maintenance practices
Your Next Steps Towards TPM
Implementing Total Productive Maintenance involves transforming your manufacturing culture. It’s way more than just fixing your machines.
Start small, think big, and focus on a single step, as that’s how even the world-class manufacturers took their first step.
Ready To Transform Your Maintenance Approach?
Start by assessing your current state.
Secure leadership support
Select your first pilot area.
Remember, Total maintenance productive success isn’t achieved overnight. It requires commitment, proper planning, and employee engagement.
What Do You Know About TPM?
Share your knowledge about TPM by writing to us on our dedicated page, which aims to facilitate learners.
Reference:
https://www.moresteam.com/lean/tpm.cfm
https://www.epa.gov/sustainability/lean-thinking-and-methods-tpm
Latest Article & Content
- Plant Inspections and lubrication schedule
- Breakdown maintenance
- Cost reduction programs
- Improving Oee in Business Operations
- Toll Production and Production Outsourcing
- Country and Work Culture in South east Asia
- Discounted Payback period
- Payback Period
- Home
- Is Defect Prevention in Lean Manufacturing?
- What is a Red Rabbit in Manufacturing?
- What is Total Productive Maintenance?
- How to Calculate OEE Performance?
- What is Total Productive Maintenance?
- Short Interval Control
- What Are the Two Types of Inventory Costs?
- Is Lean Six Sigma Worth It?
- What Is Mura and Why Do You Need to Remove It?

